|
Groundwater - water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock 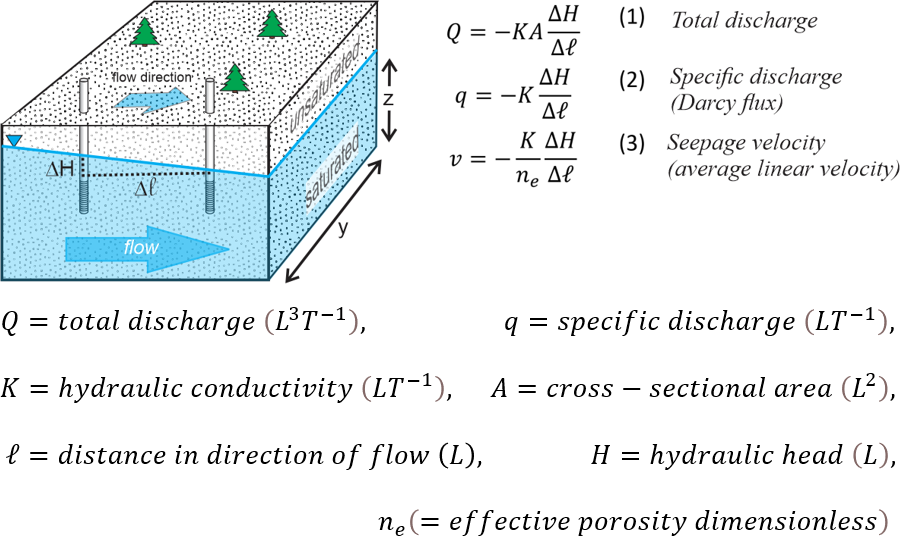
|
Freshwater - water not found in the sea; water that is not salt-water 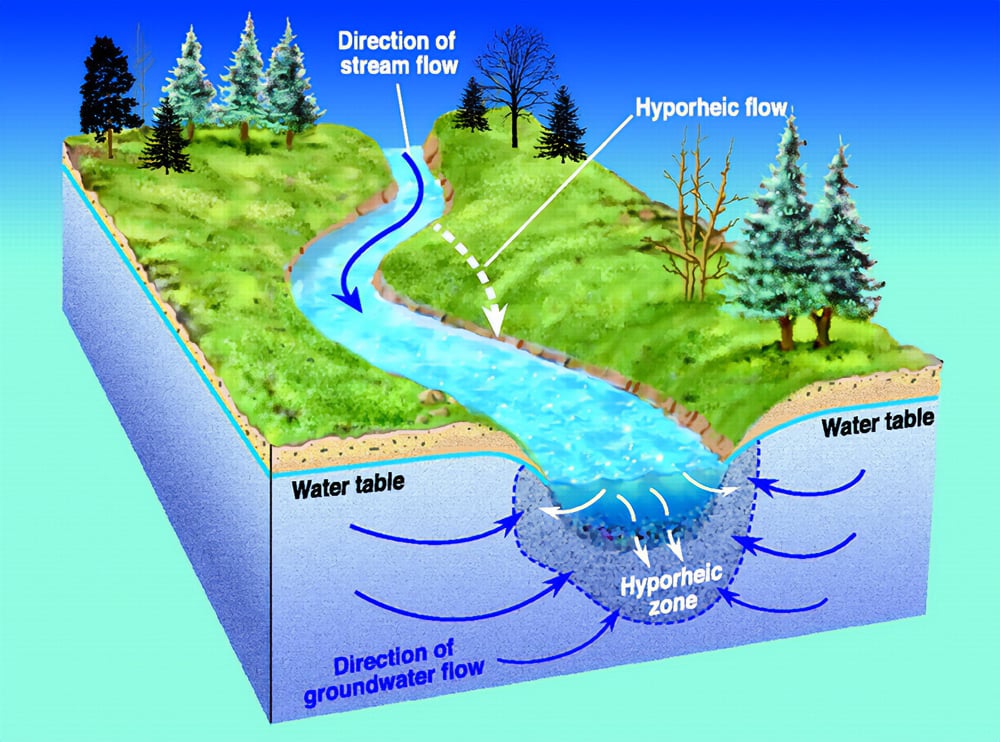 |
Groundwater moves through porous materials and fractures in rock due to hydraulic gradients. The speed and direction of flow are influenced by permeability and pressure differences. Understanding these principles is crucial for sustainable water resource management.
|
|
Groundwater - water held underground in the soil or in pores and crevices in rock 
|
Freshwater - water not found in the sea; water that is not salt-water  |
Groundwater can take years, decades, or even centuries to travel through an aquifer!
Some deep groundwater reserves, known as fossil water, have been trapped underground for thousands or even millions of years!