|
Recharge - The replenishment process that adds water to aquifers 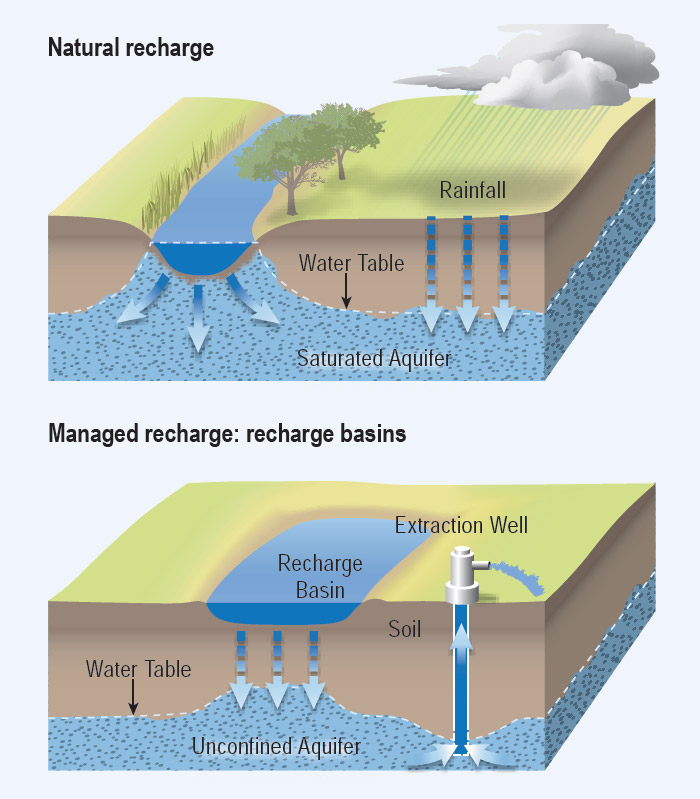
|
Discharge - The natural release of groundwater to surface environments 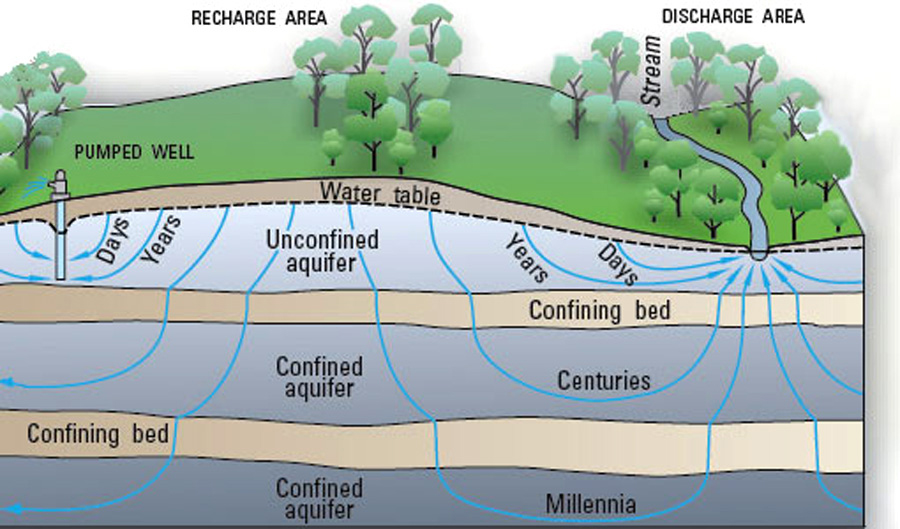 |
Groundwater recharge and discharge represent the fundamental processes that sustain aquifer systems worldwide. Recharge occurs when water from precipitation, streams, or irrigation infiltrates into aquifers, while discharge happens when groundwater emerges at springs, seeps into streams, or is extracted through wells. These complementary processes form the basis of groundwater circulation and availability.
|
|
Recharge - The replenishment process that adds water to aquifers 
|
Discharge - The natural release of groundwater to surface environments  |
Recharge rates vary dramatically worldwide!
While some desert aquifers might receive less than 1mm of recharge per year, tropical regions can experience several hundred millimeters annually. In Morocco, coastal aquifers typically receive 30-100mm of annual recharge, varying significantly by region.